In Vitro Fertilization (IVF): Big Step for a Small Wonder

Find Your Perfect Match
Answer a few questions and we'll provide you with a list of primary care providers that best fit your needs.
As frequently as the term “IVF” pops up in an Internet search for “infertility treatment,” it’s actually one of the least common treatments, representing less than 5 percent of all infertility treatments in the United States. The road to IVF (in vitro fertilization) winds through a few checkpoints first.
What is IVF?
In vitro fertilization is the joining of a woman's egg and a man's sperm in a laboratory dish for fertilization. It’s an advanced fertility treatment and typically is tried when less expensive fertility techniques have failed.
IVF is expensive, not always successful, and insurance plans vary widely on coverage. The cost for a single IVF cycle can range from $12,000 to $17,000. It often takes more than one cycle to achieve success, if at all.
Your fertility specialist, also called a reproductive endocrinologist, will order comprehensive fertility testing to evaluate your unique infertility and discuss treatment options.
Who Might IVF Help?
IVF can be used to treat infertility for the following reasons:
- Blocked, damaged or missing fallopian tubes
- Male factor infertility, including decreased sperm count or sperm motility
- Women with ovulation disorders, premature ovarian failure, uterine fibroids or endometriosis
- Genetic disorders
- Advanced maternal age
- Unexplained infertility
How Does IVF Work?
It’s best to fully understand the significant physical, financial and emotional commitment involved as you consider IVF. Your fertility specialist should be honest concerning these issues and should take time when explaining appointments, medications, success rates and procedures.
You can expect these key steps during your IVF cycle:
- Ovulation induction. Hormone medication that stimulates ovaries to produce multiple mature eggs
- Egg retrieval. Outpatient surgical procedure using ultrasound imaging to guide a hollow needle through the vagina to the ovaries to remove eggs
- Insemination and fertilization. Eggs and sperm are combined in a lab for fertilization
- Embryo culture. Fertilized eggs begin cell division to become embryos and continue to grow in the lab
- Embryo transfer. One or more embryos are placed into the uterus three to five days after egg retrieval and fertilization
If you are unable to produce eggs, your fertility specialist can suggest an egg donor. In either case, deciding on the number of embryos to transfer to your uterus is an important decision. Unused embryos may be frozen and implanted or donated at a later date.
It’s best to fully understand the significant physical, financial and emotional commitment involved as you consider IVF.
How Successful Is IVF?
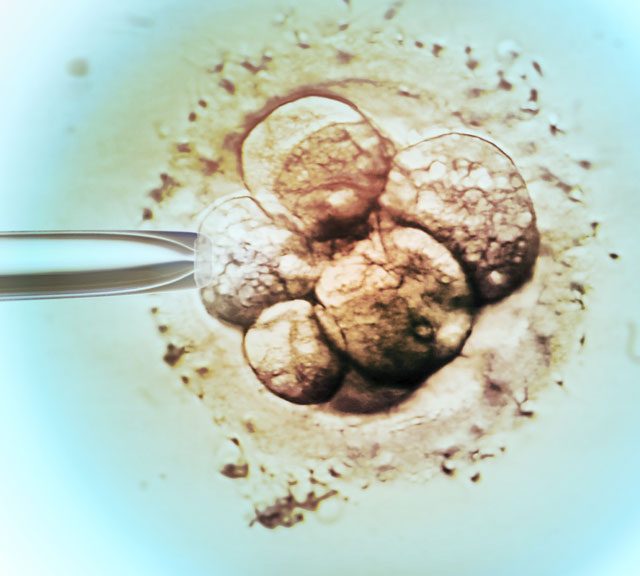
Advancements in IVF have contributed to higher success rates in the last few decades. A game changer was the development of ICSI (intracytoplasmic sperm injection), which injects a sperm directly into an egg to improve fertilization chances.
According to the Society of Assisted Reproductive Technologies (SART), the approximate chance of giving birth to a live baby after IVF is:
- 41 to 43 percent for women under age 35
- 33 to 36 percent for women ages 35 to 37
- 23 to 27 percent for women ages 38 to 40
- 13 to 18 percent for women ages over 40
Clinic success rates can vary broadly and reflect multiple factors, including complexity of cases. Live birth rate comparisons provide a more realistic view of success than pregnancy rates since not all pregnancies result in live births.
What Are IVF Risks?
Besides emotional and financial considerations, you also may want to become familiar with IVF physical risks and side effects.
IVF Risks
- Ovarian hyper-stimulation syndrome (OHSS) - a rare yet serious condition caused by fertility medications in which ovaries become swollen and painful
- Bleeding, infection or damage to bowel or bladder, or anesthesia reaction during egg retrieval
- Multiples pregnancy, which can increase risk for premature delivery and low birth weight
- Ectopic pregnancy – when a fertilized egg implants anywhere outside the uterus and is not viable
Egg Retrieval Side Effects
- Passing a small amount of fluid (may be blood-tinged) after the procedure
- Mild cramping
- Mild bloating
- Constipation
- Breast tenderness
Fertility Medication Side Effects
- Headaches
- Mood swings
- Abdominal pain and/or bloating
- Hot flashes
Find Your Perfect Match
Answer a few questions and we'll provide you with a list of primary care providers that best fit your needs.
Source: American Pregnancy Association; MedlinePlus, U.S. National Library of Medicine; RESOLVE: The National Infertility Association




